The CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) checksum error is a problem encountered by computer users, often perplexing and causing a hindrance to the booting process.
This detailed guide aims to demystify the CMOS checksum error, explore its causes, and present practical solutions, including how to reset your CMOS to get your system back up and running smoothly.
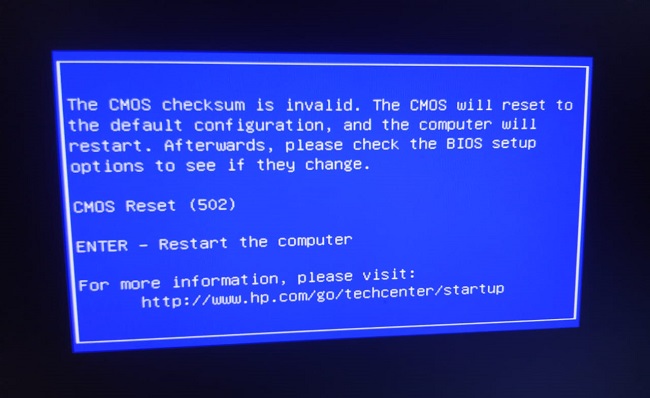
What is the Meaning of CMOS Checksum Error?
The CMOS checksum error typically appears during computer startup, displaying a message such as “CMOS checksum invalid” or similar. This error indicates a mismatch between the data stored in the CMOS and the checksum value calculated upon startup.
The CMOS, a small memory chip on the motherboard, stores system configuration details, including hardware settings and the system clock. The checksum is a value calculated from the contents of the CMOS.
If the calculated checksum doesn’t match the stored value, it suggests the data may be corrupt, triggering the error message.
Causes of the CMOS Checksum Error
Several factors can lead to a CMOS checksum error. Understanding these can help in troubleshooting and preventing future occurrences.
Battery Failure
The most common cause is a failing CMOS battery. This battery maintains the data in the CMOS memory when the computer is powered off. Over time, the battery depletes, leading to data loss or corruption.
Incorrect System Shutdown
Improper shutdowns, due to power outages or forced shutdowns, can corrupt the CMOS data, resulting in a checksum error on the next boot.
BIOS Update or Corruption
Updating the BIOS can sometimes lead to checksum errors, especially if the update process is interrupted. Additionally, BIOS corruption due to malware or hardware failure can cause this error.
Hardware Issues
Faulty hardware or incorrect hardware configurations can also lead to CMOS checksum errors. This includes problems with the motherboard, RAM, or even peripheral devices.
Methods to Fix CMOS Checksum Error
Addressing a CMOS checksum error involves a few straightforward steps, which can resolve the issue in most cases.
Check the CMOS Battery
Replace the CMOS battery if your computer is old or the battery hasn’t been changed in a while. This is often the simplest and most effective fix.
Reset BIOS Settings
Entering the BIOS setup and choosing to load default settings can resolve checksum errors caused by incorrect configurations.
Update BIOS
If the error persists, updating the BIOS to the latest version may resolve compatibility issues or bugs causing the checksum error.
Check for Hardware Issues
Inspect your computer for any hardware problems. This includes ensuring all components are correctly installed and functioning. Removing and reseating hardware can sometimes resolve the issue.
How to Reset Your CMOS
Resetting the CMOS clears the current configuration and restores the default settings, which can often resolve a checksum error. Here’s how to do it:
- Turn Off the Computer: Ensure the computer is completely powered down and disconnected from any power source.
- Access the Motherboard: Open your computer’s case to access the motherboard.
- Locate the CMOS Battery: Find the small, circular battery on the motherboard.
- Remove the Battery: Carefully remove the battery. You might need to wait a few minutes before reinserting it to ensure the CMOS is reset.
- Use the Jumper: Some motherboards have a jumper that can be used to clear the CMOS. If so, refer to the motherboard’s manual for instructions on using it.
- Reassemble and Restart: Once the battery is back in place or the jumper has been used, reassemble your computer and power it on. Enter the BIOS setup to configure any necessary settings.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for prolonging the life of your computer and preventing issues like the CMOS checksum error.
This includes cleaning dust from the interior, ensuring proper ventilation to prevent overheating, and keeping all software, especially the BIOS, up to date. Regular checks and updates can prevent compatibility issues and firmware bugs that may lead to system errors.
Understanding BIOS Updates
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is integral to the startup process and overall operation of your computer. It acts as an intermediary between the computer’s firmware and its operating system.
Periodically, motherboard manufacturers release BIOS updates to enhance functionality, add new features, fix bugs, or improve compatibility with newer hardware and software.
However, it’s important to approach BIOS updates with caution, as an incorrect update can cause system instability or even failure. Always ensure that any updates are directly from the manufacturer and match your specific motherboard model.
Safeguarding Against Power Surges
Power surges can cause sudden system shutdowns, leading to CMOS checksum errors and other hardware damage. Using a surge protector or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) can safeguard your computer from unexpected power fluctuations and outages.
A UPS also provides the added benefit of battery backup, allowing you to properly shut down your computer during a power outage.
Hardware Compatibility and Installation
Incorrectly installed or incompatible hardware can cause numerous issues, including the CMOS checksum error.
When upgrading or replacing components, ensure they are compatible with your motherboard and other system components. Proper installation is equally important; a loose connection or improperly seated component can lead to errors or hardware damage.
Staying Informed
Keeping informed about the latest hardware developments, common issues, and troubleshooting techniques can greatly assist in maintaining a healthy computer system.
Online forums, manufacturer support sites, and tech news websites are valuable resources for staying updated on potential issues and solutions.
Conclusion
The CMOS checksum error is a common issue that can be fixed with some basic troubleshooting steps. Whether it’s replacing the CMOS battery, resetting the BIOS, updating firmware, or checking hardware, these solutions can help overcome the error, allowing your system to boot normally.
Regular maintenance and proper shutdown procedures can prevent future occurrences, ensuring a smooth computing experience.
FAQ on CMOS Checksum Error
Q1: What is a CMOS checksum error?
A: A CMOS checksum error is a conflict that arises when the computer’s BIOS fails to match the checksum value of the CMOS contents. This error usually occurs at startup and indicates that the CMOS data is corrupt or has been altered unexpectedly.
Q2: What causes a CMOS checksum error?
A: The main causes include:
- Battery Failure: The most common reason, where the CMOS battery loses its charge, leading to data loss.
- Improper Shutdowns: Sudden power losses or incorrect shutdown procedures can corrupt the CMOS data.
- BIOS Updates or Corruption: Failed or interrupted BIOS updates, or corruption caused by malware or system failures, can trigger checksum errors.
- Hardware Faults: Faulty or incorrectly configured hardware can also lead to this error.
Q3: How do I fix a CMOS checksum error?
A: Solutions vary based on the underlying cause:
- Replace the CMOS Battery: This is the first step if the battery is old or suspected to be failing.
- Reset BIOS Settings: Access the BIOS setup and choose to load default settings, which can rectify misconfigurations.
- Update BIOS: Ensure the BIOS is updated to the latest version from the manufacturer’s official site.
- Inspect Hardware: Check for any hardware issues, ensuring all components are correctly installed and functioning.
Q4: How can I reset my CMOS?
A: To reset your CMOS, you can:
- Power off your computer and disconnect it from any power source.
- Open the computer case and locate the CMOS battery on the motherboard.
- Remove the battery for a few minutes, then reinsert it, or use the motherboard’s jumper switch as per the manual’s instructions to reset the CMOS.
- Reassemble your computer and restart it, entering the BIOS setup to reconfigure any necessary settings.
Q5: How often should I replace my CMOS battery?
A: The CMOS battery typically lasts for about 5 to 10 years, but this can vary based on the motherboard’s design and the battery’s quality. It’s advisable to replace the battery if you start experiencing issues like the CMOS checksum error, or if the system clock begins losing time.
Q6: Can CMOS checksum errors harm my computer?
A: While the error itself doesn’t harm the computer, it indicates issues that could lead to data loss or hardware malfunctions if not addressed. For example, incorrect BIOS configurations can cause system instability.
Q7: Is it safe to update BIOS by myself?
A: Updating the BIOS is a critical process and should only be done when necessary, and with caution. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely and ensure the update is specifically for your motherboard model. A failed update can render your motherboard inoperative.