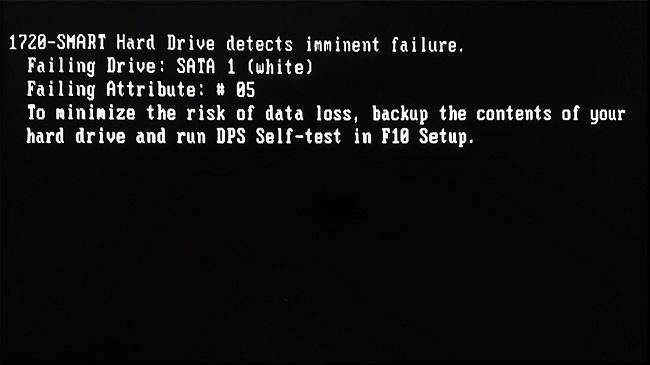
Encountering a “1720-SMART Hard Drive detects imminent failure” warning on your computer can be alarming. This message is a critical alert that indicates your hard drive is on the verge of failing.
SMART, or Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology, is a monitoring system included in computer hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) to detect and report various indicators of drive reliability.
In this detailed article, we’ll dive into the meaning behind this warning, explore the causes of a 1720-SMART hard drive imminent failure issue, and provide comprehensive steps on how to address this predicament to safeguard your data and ensure the longevity of your device.
What Does the 1720-SMART Hard Drive Imminent Failure Mean?
The 1720-SMART warning is a predictive failure analysis feature of the SMART system, designed to alert users of potential hard drive failures before they occur. It means that the hard drive has detected a significant enough error that, if not addressed, could lead to total drive failure, resulting in the loss of all data stored on the drive.
Causes of the 1720-SMART Hard Drive Imminent Failure Issue
Several factors can trigger this warning, including:
- Mechanical Wear and Tear: Over time, the physical components of a hard drive can degrade, leading to potential failure.
- Bad Sectors: These are areas of the hard drive that have been damaged and can no longer be used reliably.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage the internal components of the hard drive, leading to failure.
- Electrical Faults: Power surges or unstable power supply can harm the hard drive’s electronic components.
- Firmware Corruption: The software that controls the hard drive can become corrupted, leading to errors and potential failure.
How to Fix Imminent Failure on Your Hard Drive
Addressing an imminent hard drive failure involves a combination of immediate data backup and taking steps to either repair or replace the hard drive. Here are actionable steps you can take:
Step 1: Back Up Your Data Immediately
The first and most crucial step upon receiving this warning is to back up all important data from your hard drive. You can use an external hard drive, a cloud storage service, or another computer to secure your files.
Step 2: Check the Hard Drive’s Health
Use built-in diagnostic tools to check the health of your hard drive. For Windows, you can use the WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Command-line) tool by opening Command Prompt and typing wmic diskdrive get status. For macOS, use Disk Utility to perform a S.M.A.R.T. status check.
Step 3: Run Disk Repair Utilities
For Windows, use the CHKDSK utility to find and repair disk errors. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type chkdsk /f /r. On macOS, Disk Utility’s “First Aid” can perform similar checks and repairs.
Step 4: Consider Hard Drive Replacement
If the SMART warning persists after backing up data and attempting repairs, it’s advisable to replace the hard drive. Continuing to use a failing drive can result in total data loss.
Step 5: Update Firmware
Occasionally, updating the hard drive’s firmware can resolve minor errors or compatibility issues that might trigger the SMART warning. Check the manufacturer’s website for firmware updates.
Step 6: Monitor Hard Drive Temperature
Ensure your computer’s cooling system is functioning correctly to prevent overheating. Consider using software tools to monitor the temperature of your hard drive regularly.
In addition to addressing the immediate concern triggered by a “1720-SMART Hard Drive detects imminent failure” warning, adopting long-term strategies and proactive measures can significantly enhance the durability and reliability of your hard drives. Here’s how you can ensure the health and longevity of your data storage solutions:
Regularly Monitor Hard Drive Health
Implement a routine schedule for checking the health of your hard drives. Utilizing SMART monitoring tools or third-party software designed for hard drive diagnostics can provide real-time insights into your drive’s condition, allowing for early detection of potential issues.
Optimize Your Computer’s Environment
The physical environment plays a crucial role in the longevity of your hard drives. Ensure your computer is kept in a cool, dry place to prevent overheating and moisture damage. Proper ventilation or additional cooling systems can help maintain an optimal operating temperature.
Practice Good Data Management
Organize your data efficiently by regularly archiving old files, deleting unnecessary data, and defragmenting your hard drive (for HDDs). This not only frees up space but also reduces the workload on your hard drive, potentially extending its lifespan.
Stay Updated
Keep your operating system, drivers, and firmware up to date. Manufacturers often release updates that improve performance, fix bugs, and patch vulnerabilities, all of which can contribute to a more stable and reliable hard drive.
Consider Using SSDs
Solid-state drives (SSDs) offer a more durable alternative to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). With no moving parts, SSDs are less susceptible to mechanical failures and can provide faster data access times. Upgrading to or incorporating SSDs for your primary drive can enhance your system’s performance and reliability.
Implement a Redundant Data Backup System
Adhering to the 3-2-1 backup rule—keeping at least three total copies of your data, two of which are local but on different devices, and one copy off-site—can safeguard your data against the most severe hard drive failures. Consider cloud storage solutions for an off-site backup that is both secure and accessible.
Educate Yourself on Signs of Failure
Understanding the warning signs of hard drive failure, such as frequent freezes, disappearing data, corrupt files, and unusual noises (for HDDs), can help you take timely action to prevent data loss.
Use Encryption for Sensitive Data
Protecting your data is just as important as protecting the physical drive. Use encryption for sensitive files to ensure data security, especially in scenarios where the hard drive may need to be replaced or serviced by external parties.
Conclusion
The “1720-SMART Hard Drive detects imminent failure” warning should never be ignored. It serves as a critical alert to back up your data and address the health of your hard drive.
By understanding the causes behind this warning and following the steps outlined to mitigate the issue, you can prevent data loss and extend the lifespan of your computing device.
Remember, regular backups and periodic health checks can keep you one step ahead, ensuring your data’s safety against potential hard drive failures.